
Are you familiar with the concept of grammatical agreement in Spanish? There are two main types of agreement in Spanish: noun agreement and verb agreement. Today's lesson will provide an introduction to each.
The concept of noun agreement is the following: Since Spanish nouns are either masculine or feminine and singular or plural, their definite or indefinite articles, adjectives, and other grammatical elements must correspond in terms of these attributes. Let's take a look at a chart that demonstrates this concept with masculine and feminine singular and plural nouns and their corresponding definite and indefinite articles.
| Singular: | Plural: | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Masculine: | el chico (the boy) | los chicos (the boys) | |
| un chico (a boy) | unos chicos (some boys) | ||
| Feminine: | la chica (the girl) | las chicas (the girls) | |
| una chica (a girl) | unas chicas (some girls) |
The chart shows us the various ways to say "the" (el, los, la, las) and "a/an" (un, unos, una, unas), depending upon whether a noun is masculine or feminine and singular or plural. That said, let's keep a couple of additional points in mind regarding recognizing the number and gender of Spanish nouns and/or modifying them to achieve noun agreement.
1. Although many Spanish masculine singular nouns end in -o and many Spanish feminine nouns end in -a, this is not always the case. Therefore, less obvious nouns (e.g. el avión (the airplane) or la nube (the cloud)) require simply memorizing the gender of the noun, especially nouns that refer to inanimate objects. For this reason, Spanish students typically learn new nouns and their respective masculine or feminine definite articles simultaneously.
2. As a general rule, many nouns that end in a vowel require the addition of an -s to make them plural, while many nouns that end in a consonant become plural by adding -es. Applying this to the abovementioned nouns, el avión becomes los aviones while la nube changes to las nubes.
In addition to their articles, Spanish adjectives must also agree in terms of number and gender with the nouns they modify, with the same general spelling guidelines that we mentioned for pluralizing nouns. Let's hear how this works via some examples from our Yabla Spanish library:
Un coche bonito, unos coches bonitos. Una casa roja, las casas rojas.
A nice car, some nice cars. A red house, the red houses.
Captions 28-29, Fundamentos del Español 3 - Le Estructura de las Frases
Play Caption
unos ojos azules, inmensos...
some huge, blue eyes...
Caption 24, Extr@: Extra en español Ep. 6: El día de la Primitiva - Part 2
Play Caption
As you delve further into more complex Spanish grammar such as direct object pronouns, you will see how the number and gender of Spanish nouns continue to exert their influence.
Verb agreement in Spanish refers to the fact that Spanish verbs need to be conjugated in accordance with their respective subjects or subject pronouns, agreeing in number (singular or plural) and person (first, second, or third). Although this concept exists in English, it is much simpler due to the fact that there are less subject pronouns in English (seven vs. thirteen in Spanish) and far less verb forms. For example, for all of the seven English subject pronouns, there are only two verb forms, as we see below:
Subject Pronoun:
I: speak
you: speak
he: speaks
she: speaks
we: speak
they: speak
it: speaks
In Spanish, on the other hand, there are thirteen subject pronouns and many corresponding conjugations. Additionally, the manner in which each verb is conjugated depends upon which of the three common verb categories (-ar, -er, and -ir) it falls into, and many verbs are irregular, making verb agreement in Spanish significantly more complex. With this in mind, let's take a look at a chart with the conjugations of three common regular verbs, one from each category, in the present indicative tense:
| Subject Pronoun: | hablar: | comer: | subir: |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | hablo | como | subo |
| tú | hablas | comes | subes |
| vos | hablás | comés | subís |
| él/ella/usted | habla | come | sube |
| vosotros/vosotras | habláis | coméis | subís |
| nosotros/nosotras | hablamos | comemos | subimos |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | hablan | comen | suben |
If that doesn't seem nuanced enough, keep in mind that that was just one of the sixteen Spanish verb tenses, each of which has its own specific manner of conjugating verbs in order to ensure verb agreement.
We hope that these explanations have given you a better idea about the concept of noun and verb agreement in Spanish, which are essential to understanding Spanish sentences and constructing your own. Don't forget to write us with your questions and comments.

How do you say "you" in Spanish? In contrast to English, where "you" just say "you," there are a plethora of different ways to say this in Spanish, which we'll explore today.
Subject pronouns in Spanish (e.g. yo (I), tú (you), él/ella (he/she), etc.) are the most basic way to say "you." While in English, "you" is the only second person subject pronoun, in Spanish, there are five different ones, and the one you choose will depend on such factors as whether you are addressing one or more than one person, if the situation is more or less formal, and what region you are in. Let's take a closer look.
Simply put, tú means "you" for speaking to just one person in less formal situations, such as speaking to someone you already know. This is the most common familiar second person subject pronoun in most Spanish-speaking countries.
Tú hablas obviamente muy bien el español, pero
You obviously speak Spanish very well, but
Caption 10, Carlos y Xavi Part 4 Tradiciones y comida de Barcelona
Play Caption
Vos is used in a similar fashion as tú in certain countries/regions. It is heard predominantly in Argentina and Uruguay but also in certain areas of Paraguay, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, Mexico, and Venezuela.
¿Y vos hablás de mí?
And you talk about me?
Caption 51, Muñeca Brava 18 - La Apuesta - Part 11
Play Caption
Usted is used to address just one person in more formal situations. Examples might be when you don't know someone and wish to be polite or, perhaps, when addressing an elder.
¿Usted habla del ganso ese? -Sí.
Are you talking about that goose? -Yes.
Caption 54, Muñeca Brava 1 Piloto - Part 10
Play Caption
Vosotros and vosotras are employed to address more than one person informally and are thus the plural equivalent of tú. Vosotros is used for a group of all males or a mixed male-female group, while vosotras is used for more than one person when everyone is female. Vosotros and vosotras are only used in Spain.
Vosotros habláis.
You [plural] speak.
Caption 11, Fundamentos del Español 7 - Ser y Estar
Play Caption
Ustedes is used in all Spanish-speaking countries except Spain as the only plural form of saying "you," regardless of formality. However, in Spain, it is used more formally as the plural equivalent of usted (to distinguish it with the less formal vosotros/as).
Y es que hay muchas diferencias entre la forma en que ustedes hablan el español
And it's just that there are a lot of differences between the way in which you guys speak Spanish
Captions 44-45, Carlos y Xavi Part 2 Ustedes y Vosotros
Play Caption
All of the aforementioned subject pronouns in these clips have been translated as "you" with the exception of the last one, which was translated with the informal "you guys" to emphasize that it is directed to more than one person. However, it would be perfectly acceptable to translate ustedes as merely "you" since English often employs this pronoun to address multiple people.
For an abundance of additional information on these five subject pronouns for "you" in Spanish, we recommend Carlos' five-part video series on the Tuteo, ustedeo y voseo.
As you may have noticed in the examples above, all of which contain the simple present form of the verb hablar (to speak), the form of "you" utilized affects the verb conjugation. Although this happens in every verb tense in Spanish, let's start by taking a look at the simple present tense conjugations of three common Spanish verbs with their various "you" forms highlighted.
| Personal Pronoun | Hablar | Comer | Subir |
| Yo | hablo | como | subo |
| Tú | hablas | comes | subes |
| Vos | hablás | comés | subís |
| Él/ella | habla | come | sube |
| Usted | habla | come | sube |
| Nosotros/nosotras | hablamos | comemos | subimos |
| Ellos/ellas | hablan | comen | suben |
| Ustedes | hablan | comen | suben |
| Vosotros/vosotras | habláis | coméis | subís |
You will note that the verb conjugations for all of the five forms of "you" in Spanish differ from one another. Additionally, the conjugation for usted is the same as the conjugation for the third person singular él/ella (he/she) while the conjugation for ustedes is the same as the third person plural conjugation for ellos/ellas (they). Additionally, the conjugations for vos and vosotros/as are the same for -ir verbs.
Remember that in Spanish, you don't necessarily need to explicitly say the subject pronoun in order to know which one is in use because the verb tenses themselves make that clear. That said, let's examine a few examples with different forms of "you" and the verb saber (to know).
¿Sabéis qué es un volcán?
Do you know what a volcano is?
Caption 18, Aprendiendo con Silvia Los volcanes
Play Caption
Ay, ¿sabes qué?
Oh, you know what?
Caption 21, Club 10 Capítulo 1 - Part 1
Play Caption
¿Sabe que no me parece suficiente?
Do you know that it doesn't seem like enough to me?
Caption 62, Confidencial: El rey de la estafa Capítulo 3 - Part 3
Play Caption
Despite the absence of subject pronouns, you can tell from the verbs' conjugation that the first example refers to vosotros, the second example refers to tú, and the third example refers to usted, and for this reason, all three have been translated with "you know." While the third example could technically refer to él or ella as well since the conjugations for all three are the same, the context (one person speaking directly to another rather than talking about anyone else) alerts you that the speaker is addressing the other person as usted.
Subject pronouns are not the only way to represent the word "you" in Spanish. Other types of Spanish pronouns (direct object, indirect object, and prepositional) also mean "you." Let's see which of each of these types of pronouns correspond with which "you" subject pronouns:
| Subject Pronoun | Direct Object Pronoun | Indirect Object Pronoun | Prepositional Pronoun |
| Tú | te | te | ti |
| Vos | te | te | vos |
| Usted | lo, la | le | usted |
| Ustedes | los, las | les | ustedes |
| Vosotros/as | os | os | vosotros/as |
While we won't delve too deeply into these topics, we will provide a brief summary of each of them and give you some examples.
Direct object pronouns take the place of the direct object (the recipient of an action) in a sentence and answer the question of "what" or "who." Let's see a couple of examples:
Vale, no... no os veo... no os veo con mucha...
OK, I don't... I don't see you... I don't see you with a lot...
Caption 39, Escuela BCNLIP Clase con Javi: el futuro - Part 3
Play Caption
Los veo en el próximo video.
See you in the next video.
Caption 44, Manos a la obra Postres de Minecraft
Play Caption
In both examples, the translation of the direct object pronoun is "you." In the first, os takes the place of vosotros, and in the second, los takes the place of ustedes.
Indirect object pronouns answer the question "to who/whom" or "for who/whom" an action is carried out. Let's take a look:
De verdad, yo le doy la plata que tengo ahí;
Seriously, I'll give you the money I have there;
Caption 25, Confidencial: Asesino al Volante Capítulo 1 - Part 1
Play Caption
Otra recomendación que les puedo hacer es que traigan zapatos para el agua,
Another recommendation that I can give you is to bring water shoes,
Captions 35-36, Alan x el mundo Mi playa favorita de México! - Part 2
Play Caption
In the first example, le lets you know that the speaker will give the money "to" usted, while in the second, the recommendation is being given "to" ustedes. While the indirect object pronouns in these two captions have been translated with simply "you," the translator might also have opted for "I'll give the money I have there to you" and/or "Another recommendation that I can give to you is to bring water shoes."
To learn more about indirect and direct object pronouns, check out this two-part lesson on How to Use Direct and Indirect Object Pronouns.
Prepositional pronouns are pronouns that follow a preposition (words like para (for), de (of, about), en (in, about), etc.) in a sentence.
Este libro es para ti. Este libro es para vos.
This book is for you. This book is for you.
Captions 47-48, Carlos y Cyndy Uso del Voseo en Argentina
Play Caption
y hoy, he preparado para ustedes estos objetos
and today, I've prepared these objects for you
Caption 3, Ana Carolina El uso correcto de los adjetivos
Play Caption
Interestingly, ti is the only prepositional pronoun meaning "you" that differs in form from its corresponding subject pronoun.
We hope that this lesson has made clear the many different ways that Spanish expresses the concept of "you." That's all for today... and don't forget to leave us your suggestions and comments.

The present subjunctive in Spanish is one of the many verb tenses in the Spanish subjunctive mood. The subjunctive mood is one of three moods in Spanish (the indicative, the imperative, and the subjunctive) that indicates the presence of doubt, emotion, or subjectivity, in contrast to the indicative, which states facts. The focus of today's lesson will be the conjugation of the Spanish present subjunctive tense.
Before going on to conjugation, let's see an example of the present subjunctive in Spanish, which typically appears after the present indicative in dependent clauses connected by a coordinating conjunction such as que (that). As a simple example, if you say, "I hope [that] you practice at home" with ustedes (plural you) in Spanish, the correct manner of doing so would be
espero que practiquen en su casa
I hope you guys practice at home
Caption 60, Lecciones de guitarra Con Cristhian - Part 3
Play Caption
rather than espero que practican en su casa because the verb tense changes from the indicative (practican) to the subjunctive (practiquen) due to the "hope" regarding whether the action will take place. In another lesson, we will explore the many scenarios in which the Spanish subjunctive mood comes into play.
The first step in conjugating most verbs in the present subjunctive is to recall the present indicative yo (I) form of the verb. We then remove the -o in order to get the stem and add the corresponding endings for -ar and -er/-ir verbs, which we can think of as the "opposite" of the endings for each verb class in the present indicative.
Let's use the aforementioned formula to get the stems for three of the most common regular verbs:
| Verb | Yo Form | Stem |
|---|---|---|
| hablar (to speak) | hablo | habl- |
| comer (to eat) | como | com- |
| subir (to go up) | subo | sub- |
Now, let's look at the present subjunctive endings for -ar vs. -er/-ir verbs:
| Personal Pronoun: | -ar Verbs: | -er/-ir Verbs: |
|---|---|---|
| yo | -e | -a |
| tú | -es | -as |
| él/ella/usted | -e | -a |
| nosotros/as | -emos | -amos |
| vosotros/as | -éis | -áis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | -en | -an |
Armed with this information, we can easily conjugate these verbs in the present subjunctive in Spanish. You will note that in the present subjunctive, the yo form and the él/ella/usted form are exactly the same.
| Personal Pronoun: | hablar: | comer: | subir: |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | hable | coma | suba |
| tú | hables | comas | subas |
| él/ella/usted | hable | coma | suba |
| nosotros/as | hablemos | comamos | subamos |
| vosotros/as | habléis | comåis | subáis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | hablen | coman | suban |
Now, let's see these Spanish present subjunctive verbs in action:
Porque quiero que hablemos de negocios.
Because I want us to talk about business.
Caption 3, Muñeca Brava 8 Trampas - Part 6
Play Caption
¿'tas listo? -¿Qué querés que yo coma lo mismo?
You ready? -What, do you want me to eat the same thing?
Caption 43, Factor Fobia Cucarachas - Part 1
Play Caption
Dígale que no suba.
Tell him not to come up.
Caption 43, Muñeca Brava 33 El partido - Part 6
Play Caption
Note that the in the vast majority of cases, even verbs with spelling changes in the yo form will follow this very same formula for obtaining their stems/conjugations. Let's see several examples:
| Verb | Yo Form | Stem |
| caber | quepo | quep- |
| coger | cojo | coj- |
| conocer | conozco | conozc- |
| decir | digo | dig- |
| hacer | hago | hag- |
| poner | pongo | pong- |
| salir | salgo | salg- |
| tener | tengo | teng- |
| traer | traigo | traig- |
| ver | veo | ve- |
Present Subjunctive Conjugations:
caber (to fit): quepa, quepas, quepa, quepamos, quepáis, quepan
coger (to take): coja, cojas, coja, cojamos, cojáis, cojan
conocer (to know): conozca, conozcas, conozca, conozcamos, conozcáis, conozcan
decir (to say): diga, digas, diga, digamos, digáis, digan
hacer (to make/do): haga, hagas, haga, hagamos, hagáis, hagan
poner (to put): ponga, pongas, ponga, pongamos, pongáis, pongan
salir (to go out): salga, salgas, salga, salgamos, salgáis, salgan
tener (to have): tenga, tengas, tenga, tengamos, tengáis, tengan
traer (to bring): traiga, traigas, traiga, traigamos, traigáis, traigan
ver (to see): vea, veas, vea, veamos, veáis, vean
We will now hear a couple of these in context:
Lo mejor es que tengan sala de estudio
The best thing is for them to have a study room
Caption 45, Club de las ideas La biblioteca
Play Caption
Bueno, te invito ahora a que conozcas el teatro.
Well, now I invite you to see the theater.
Caption 24, El teatro. Conversación con un doble de acción.
Play Caption
Let's examine several categories of stem-changing verbs that behave slightly differently in the present subjunctive in Spanish:
An example of this category is querer (to want), for which the yo form is quiero. While the stem for this verb is indeed quier- as usual, the stem change does not take place in the nosotros/as and vosotros/as forms, which use the stem of the infinitive (removing the -ar or -er) as follows:
quiera, quieras, quiera, queramos, queráis, quieran.
Additional verbs that fall into this category include: cerrar (to close), entender (to understand), and perder (to lose).
One example is volver (to return), and the yo form is vuelvo. The stem for this verb is vuelv-, but as with the previous category, there is no stem change in the nosotros/as and vosotros/as forms, which also take the stem from the infinitive:
vuelva, vuelvas, vuelva, volvamos, volváis, vuelvan
Some other verbs in this category are: poder (to be able), contar (to tell), volver (to return), and encontrar (to find).
An example would be sentir (to feel). As in the first category, these verbs change stems in all forms except for nosotros/as and vosotros/as. With -ir verbs, however, the -ie changes to an -i, as follows:
sienta, sientas, sienta, sintamos, sintáis, sientan
Verbs that work similarly include repetir (to repeat) and preferir (to prefer).
The verb dormir (to sleep) falls into this category in which verbs change stems in all forms except nosotros/as and vosotros/as, where the -o changes to a -u:
duerma, duermas, duerma, durmamos, durmáis, duerman
The verb morir (to die) also belongs to this class of verbs.
Let's listen to a couple of examples of such stem-changing verbs in the present subjunctive in Spanish:
lo mejor sería que vuelvas al convento.
the best thing would be for you to return to the convent.
Caption 15, Muñeca Brava 33 El partido - Part 7
Play Caption
Espero que ahora entiendan mejor
I hope that you now understand better
Caption 56, Carlos explica Diminutivos y Aumentativos Cap 2: Definiciones generales
Play Caption
To make matters a bit more complicated, some verbs in the Spanish present subjunctive change spelling in order to maintain their pronunciation, and some verbs change both stems and spelling! Let's take a look at these additional verb categories.
It is worth noting that the g in verbs ending in -ger and -gir changes to a j in the Spanish present subjunctive, for example, in the aforementioned verb coger (to get). However, this doesn't really deviate from our formula since the present indicative yo form of coger is cojo. Other verbs that follow this pattern in Spanish include corregir (to correct), elegir (to choose), and recoger (to pick up).
corregir: corrija, corrijas, corrija, corrijamos, corrijáis, corrijan
elegir: elija, elijas, elija, elijamos, elijáis, elijan
recoger: recoja, recojas, recoja, recojamos, recojáis, recojan
In the Spanish present subjunctive, verbs ending in -car change their final consonant to -qu, verbs ending in -gar change to -gu, and -zar verbs' z changes to a c. Let's take a look at verbs in each of these categories:
sacar (to take out): saque, saques, saque, saquemos, saquéis, saquen
tocar (to take): toque, toques, toque, toquemos, toquéis, toquen
cargar (to charge): cargue, cargues, cargue, carguemos, carguéis, carguen
pagar (to pay): pague, pagues, pague, paguemos, paguéis, paguen
lanzar (to throw): lance, lances, lance, lancemos, lancéis, lancen
empezar (to start): empiece, empieces, empiece, empecemos, empecéis, empiecen
As you can see, the verb empezar changes both stems (-e to -ie) and its final consonant (z to c) in the Spanish present subjunctive.
Let's hear some examples of verbs with spelling changes in the Spanish present subjunctive:
Es que no necesito que me recojas hoy.
It's just that I don't need you to pick me up today.
Caption 52, Los Años Maravillosos Capítulo 9 - Part 6
Play Caption
Bueno, ¿tú me aconsejas que comience a escribir ya con todas estas inquietudes que tengo?
Well, do you advise me to start writing now with all these concerns that I have?
Captions 68-69, Escribiendo un libro Algunos consejos sobre cómo comenzar - Part 2
Play Caption
Although you have seen that there are a lot of nuances to conjugating verbs in the present subjunctive in Spanish, there are only six verbs that are considered truly irregular. We have provided their conjugations here:
| Personal Pronoun: | dar | estar | haber | ir | ser | saber |
| yo | dé | esté | haya | vaya | sea | sepa |
| tú | des | estés | hayas | vayas | seas | sepas |
| él/ella/usted | dé | esté | haya | vaya | sea | sepa |
| nosotros/as | demos | estemos | hayamos | vayamos | seamos | sepamos |
| vosotros/as | deis | estéis | hayáis | vayáis | seáis | sepáis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | den | estén | hayan | vayan | sean | sepan |
Note that the yo and él/ella/usted conjugations of the verb dar, dé, has an accent on the e to distinguish it from the preposition de (of/from).
Let's conclude by hearing a couple of these irregular verbs in the Spanish present subjunctive in action:
Espero que sea una bonita sorpresa.
I hope that it's a nice surprise.
Caption 11, NPS No puede ser 1 - El concurso - Part 8
Play Caption
Dígame algo que no sepa.
Tell me something I don't know.
Caption 3, Los Años Maravillosos Capítulo 7 - Part 4
Play Caption
And speaking of learning new things, we hope you've found this lesson on conjugating verbs in the Spanish present subjunctive helpful! To hear a bunch more verbs conjugated in the Spanish present subjunctive, we recommend this video on Subjunctivo y sentimientos (Subjuntive and Feelings), and don't forget to leave us your suggestions and comments.

What is the present perfect tense in Spanish? Despite its name in English, the Spanish present perfect tense is actually one of the past tenses in Spanish, which indicates that one "has done" some action within some specific period of time. This lesson will examine how to conjugate this useful Spanish tense as well as providing examples of when to use it.
The present perfect tense in Spanish is relatively easy to conjugate. To do so, we should remember a simple formula: haber in present tense + participle. Let's first take a look at the present conjugation of the verb haber, which corresponds to the English "has" or "have" in the present perfect:
| Personal Pronoun: | Conjugation of Haber: |
| yo | he |
| tú | has |
| él/ella/usted | ha |
| nosotros/as | hemos |
| vosotros/as | habéis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | han |
Now, let's examine how to conjugate the participle form of verbs in Spanish, which corresponds to English words with endings like -ed or -en, such as "taken," "looked," "baked," etc.
Conjugating the participle with -ar verbs:
Take the infinitive, remove the -ar, and add the suffix -ado:
hablar: hablado (to talk/speak: talked/spoken)
mirar: mirado (to watch: watched)
comenzar: comenzado (to start/begin: started/begun)
bailar: bailado (to dance: danced)
Conjugating the participle with -er and -ir verbs:
Take the infinitive, remove the -er or -ir, and add the suffix -ido:
comer: comido (to eat: eaten)
aprender: aprendido (to learn: learned)
recibir: recibido (to receive: received)
subir: subido (to rise/go up: risen/gone up)
Irregular Participles:
There are several irregular participle forms in Spanish that it would definitely be helpful to memorize. Here are several:
abrir: abierto (to open: opened)
cubrir: cubierto (to cover: covered)
decir: dicho (to say: said)
escribir: escrito (to write: written)
hacer: hecho (to do: done)
morir: muerto (to die: died)
poner: puesto (to put: put)
romper: roto (to break: broken)
resolver: resuelto (to resolve: resolved)
satisfacer: satisfecho (to satisfy: satisfied)
ver: visto (to see: seen)
volver: vuelto (to return/returned)
Now that we know how to conjugate the auxiliary verb haber as well as the participle, we can conjugate verbs in and formulate sentences using the present perfect in Spanish.
For example, if we wanted to say, "I have spoken," we'd take the form of the verb haber that corresponds with yo (he) and the participle of the verb hablar (to speak), hablado, to get: Yo he hablado. And, we could take hemos (we have) along with the irregular participle abierto (opened) to get Hemos abierto la puerta (We've opened the door).
Ahora que hemos aprendido (Now that we've learned) how to conjugate verbs in the present perfect tense in Spanish, we should think about when to use it. Just like the present perfect in English, we use the Spanish present perfect to describe actions that have been completed within a certain period of time. As previously mentioned, because these actions were completed in the past, however recent, the present perfect is considered a past tense in Spanish, in which it is known as el pretérito perfecto (literally the "past" or "preterite perfect"). With this in mind, let's take a look at some examples:
Ya hemos visto que reciclar contribuye de forma importante,
We have already seen that recycling contributes in an important way,
Caption 23, 3R Campaña de reciclaje - Part 3
Play Caption
¿Pero se han preguntado alguna vez cómo se cultivan y se comercializan?
But have you ever wondered how they are grown and sold?
Captions 75-76, 75 minutos Del campo a la mesa - Part 16
Play Caption
Hoy ha llovido todo el día.
"Hoy ha llovido todo el día" [Today it has rained the whole day].
Caption 69, Carlos explica El pretérito Cap. 2: Perfecto compuesto I
Play Caption
The examples above entail specific but different time periods. When the speaker says Ya hemos visto (We have already seen) in the first example, he is referring to us having already seen the importance of recycling in that video. In the second caption, the speaker asks if the people to whom he is speaking have ever (alguna vez) wondered, in their entire lives. And finally, this third example of the present perfect in Spanish explains what has happened that day.
It is important to note that while sentences in the present perfect often contain such references to the time period they describe as todo el día (all day), alguna vez (ever), ya (already), etc., this is not always the case. For example, in an effort to find out if "you have (ever) traveled to Spain," someone might simply ask: ¿Has viajado a España?
Sometimes, Spanish speakers from Spain in particular use the present perfect to talk about actions in the recent past in situations in which English speakers would most likely use the past tense and Latin Americans would probably use the Spanish preterite. Let's look at an example:
Hola, soy Ariana Moreno y he dormido fatal. He pasado una mala noche.
Hello, I'm Ariana Moreno, and I've slept horribly. I've had a bad night.
Captions 1-3, Ariana Cita médica
Play Caption
Although the translators at Yabla opted to literally translate he dormido (I've slept) and he pasado (I've spent) with the present perfect in English, the English version sounds a bit awkward in this context because an English speaker would almost always say "I slept horribly. I had a bad night" when referring to the previous night. A Spanish-speaker from Central or South America, on the other hand, might say: "Dormí fatal. Pasé una mala noche" in the preterite. Let's look at another example:
Pues nada, que ha empezado el día superbién, se ha levantado a las ocho, ha desayunado en la cafetería al lado de la escuela como siempre, ha venido a clase, hemos tenido la clase como todos los lunes.
Well, she's started the day very well, she's gotten up at eight, she's had breakfast in the cafeteria next to the school as always, she's come to class, we've had the class like every Monday.
Captions 6-10, El Aula Azul Conversación: Un día de mala suerte
Play Caption
The caption above illustrates once again that, although the same is not true in English, when talking about the very recent past (typically the same day or perhaps the previous night), Spanish speakers from Spain are much more likely to employ the present perfect tense.
We hope that this lesson has made it clear how to conjugate and use the present perfect tense in Spanish. For further explanation and examples, check out Carlos' video on El pretérito compuesto, or "Compound perfect," which is yet another name for the present perfect in Spanish, and don't forget to leave us your suggestions and comments.

How do we talk about an action in progress in Spanish? We use the Spanish present progressive tense, which we'll explore in this lesson.
What is present progressive in Spanish? Simply put, the present progressive tense in Spanish describes actions that are unfolding as we speak, at this moment. Also called the present progressive, its English equivalent includes some form of the verb "to be" in present tense along with the gerund, or -ing form, of a verb. Some examples include: "I'm reading," "You are watching TV," or "We are eating dinner." The Spanish present progressive, which we'll learn to conjugate, takes a very similar form.
So, when exactly do we use the present progressive tense in Spanish? And, what's the difference between the simple present and the Spanish present progressive? This can be a bit confusing since there is some overlap in terms of their English translations at times. Let's take a look:
¿Qué hacés vos acá?
What are you doing here?
-¿Cómo qué hago? Corro.
-What do you mean, what am I doing? I'm running.
Captions 65-66, Cuatro Amigas - Piloto
Play Caption
Although, much like the present progressive, the simple present tense in Spanish can sometimes be translated into English using the -ing form to say that one "is doing" something in the present, the Spanish simple present tense is also used to describe actions one does on a habitual basis:
¿Y los sábados y domingos, qué haces?
And on Saturdays and Sundays, what do you do?
Caption 19, Español para principiantes - Los días de la semana
Play Caption
That said, if you really want to emphasize and/or remove any doubt that an action is in progress or happening at this moment, it's necessary to use the Spanish present progressive:
Silvia, ¿qué estás haciendo?
Silvia, what are you doing?
-Estoy cocinando.
-I'm cooking.
Captions 31-32, El Aula Azul - Actividades diarias: En casa con Silvia
Play Caption
In fact, this last caption is from a video by El Aula Azul that simply and clearly demonstrates the difference between the simple present tense and the present progressive tense in Spanish.
Now that you know when to use the present progressive in Spanish, let's learn how to conjugate present progressive verbs in Spanish. To start, let's review (or learn!) the simple present conjugation of the verb estar (to be), which will convey the idea of "am" or "are":
Yo estoy (I am)
Tú estás (You are)
Él/ella/usted está (He, she is/you are)
Nosotros/nosotras estamos (We are)
Vosotros/vosotras estáis (You are [plural])
Ellos/ellas/ustedes están (They/you [plural] are)
Next, we'll need to break up infinitive Spanish verbs into two categories, verbs that end in -ar and verbs that end in either -er or -ir, in order to form their gerunds (gerundios).
To form the gerund for regular -ar verbs, we'll take the verb's stem (the part before the -ar) and add the suffix -ando. For example, for hablar (to talk), we take the stem habl- and add -ando to get hablando. Let's take a look at a few examples of regular -ar verbs in the present progressive tense in Spanish:
Entonces, en este momento, ¿veis?,
So, right now, you see?
está hablando con su madre por teléfono.
He's talking to his mom on the phone.
Captions 60-61, Clase Aula Azul - Información con subjuntivo e indicativo
Play Caption
Eh... estoy buscando a Milagros.
Um... I am looking for Milagros.
Caption 6, Muñeca Brava - 39 Verdades
Play Caption
Estamos caminando aquí en Bleeker Street
We are walking here on Bleeker Street
Caption 72, Eljuri - "Fuerte" EPK
Play Caption
Conjugating regular -er and -ir verbs in the present progressive Spanish tense is just as easy! Simply take the stem (remove the -er or -ir) and add the suffix -iendo. Thus, for correr (to run), we have corr- plus -iendo to get corriendo, and for vivir (to live), we take viv- plus -iendo for viviendo. Let's look at a few more examples:
¿Por qué estás comiendo basura?
Why are you eating garbage?
Caption 9, Kikirikí - Agua
Play Caption
Está subiendo, está subiendo la rama.
He's climbing, he's climbing the branch.
Caption 98, Animales en familia - Un día en Bioparc: Coatís
Play Caption
¿Dónde estáis vendiendo aceite?
Where are you selling oil?
Caption 1, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa
Play Caption
Although the Spanish present progressive tense is arguably one of the easier verbs to learn to conjugate in Spanish, there are some irregular verbs, of course, which fall into a few categories. Let's examine those categories of verbs with irregular conjugations in the Spanish present progressive.
Verbs with the endings -aer, -eer, -oir, and -uir change from -iendo to -yendo in the Spanish present progressive. Here are some examples:
traer: trayendo (to bring/bringing)
caer: cayendo (to fall/falling)
leer: leyendo (to read/reading)
creer: creyendo (to believe/believing)
construir: construyendo (to build/building)
huir: huyendo (to escape/escaping)
oír: oyendo (to hear/hearing)
Interestingly, the present progressive form of the verb ir (to go) is also yendo:
Sí, me venía a despedir porque ya me estoy yendo.
Yes, I came to say goodbye because I'm leaving now.
Caption 90, Muñeca Brava - 39 Verdades
Play Caption
Some verbs that change stems in the Spanish simple present tense also have an irregular form in the Spanish present progressive. Verbs whose stems change from -e to -ie (e.g. sentir becomes yo siento, tú sientes, etc.) or -e to -i (vestir changes to yo visto, tú vistes, etc.) tend to change stems from an -e to an -i in the Spanish present progressive as well, while maintaining the suffix -iendo. Let's take a look at some common examples:
sentir: sintiendo (to feel/feeling)
preferir: prefiriendo (to prefer/preferring)
mentir: mintiendo (to lie/lying)
vestir: vistiendo (to dress/dressing)
seguir: siguiendo (to follow/following)
conseguir: consiguiendo (to get/getting)
On the other hand, verbs that change from an -o to a -ue in the simple present often change from an -o to a -u in the Spanish present progressive while maintaining their regular ending (-iendo). Examples include poder ("to be able," which morphs into yo puedo, tú puedes, etc.), dormir ("to sleep," which becomes yo duermo, tú duermes, etc.), and morir ("to die," which transforms to yo muero, tú mueres, etc.). Let's look:
poder: pudiendo (to be able/being able)
dormir: durmiendo (to sleep/sleeping)
morir: muriendo (to die/dying)
Verbs in this fourth category also change from -e to -i in the simple present (e.g. reír, or "to laugh," becomes yo río, tú ríes, etc.) but also have an -e before the -ir ending. In this case, the -e is dropped, while the ending -iendo is maintained, as follows:
reír: riendo (to laugh/laughing)
sonreír: sonriendo (to smile/smiling)
freír: friendo (to fry/frying)
The aforementioned irregular verbs in the present progressive in Spanish by no means constitute an exhaustive list, and although the rules that dictate which verbs are irregular might seem daunting, with increased exposure to Spanish, conjugating such irregular verbs in the present progressive in Spanish should become intuitive in no time!
Let's conclude today's lesson by looking at an example from each of the aforementioned categories of irregular present progressive verbs in Spanish:
Ellos están construyendo la puerta de entrada al santuario de burros.
They're building the entry gate to the donkey sanctuary.
Caption 25, Amaya - Voluntarios
Play Caption
Esa mujer nos está mintiendo y quiero saber por qué.
That woman is lying to us and I want to know why.
Caption 42, Confidencial: El rey de la estafa - Capítulo 4
Play Caption
¡Aldo, tu hermano se está muriendo
Aldo, your brother is dying,
y a vos lo único que te interesa es la herencia!
and the only thing that interests you is the inheritance!
Caption 63, Yago - 3 La foto
Play Caption
Se está riendo de todos nosotros.
He's laughing at all of us.
Caption 28, Los casos de Yabla - Problemas de convivencia
Play Caption
That's all for today. For more information on the present progressive Spanish tense, check out our latest video from El Aula Azul on that very topic! And don't forget to leave us your suggestions and comments.

What are reflexive verbs in Spanish? A reflexive verb is a verb in which the subject (person or thing that completes the action) and object (person or thing that receives the action) are one and the same. In other words, the action "reflects back" onto the subject, or entails something one does to or for him or herself. It is no wonder then, that many of the things we "do to ourselves" in our daily routines (e.g. shaving ourselves, washing ourselves, etc.) fall into the category of reflexive Spanish verbs.
How can we recognize Spanish reflexive verbs? The main way to distinguish reflexive verbs in Spanish is by the fact that they all end in the pronoun se in their infinitive form. To take a very simple example, while the verb hablar means "to talk," hablarse is a reflexive verb meaning "to talk to oneself." However, the translations for reflexive verbs in Spanish aren't always so straightforward.
As we often say just "I shave" or "I wash" in lieu of "I shave/wash myself," the English translations of Spanish reflexive verbs won't always include pronouns like "myself," "yourself," etc. In other cases, the meanings of verbs like parecer (to seem) completely change in their reflexive forms (parecerse means "to look like"). And so, as there are a lot more reflexive verbs in Spanish than in English, many of which may not "seem" reflexive, with increased exposure to Spanish, we will learn which English concepts are expressed with Spanish reflexive verbs.
To conjugate reflexive verbs in Spanish, we must memorize the reflexive pronouns that correspond to each personal pronoun: yo (I), tú (you), etc.. Reflexive pronouns are most often placed before the verb, which is conjugated "as usual" (in the same way as its non-reflexive form). To demonstrate this, let's take a look at the reflexive pronouns and the simple present conjugation of the regular verb despertar (to wake up). We will then show you the conjugation of its reflexive form (despertarse).
| Personal Pronoun | Reflexive Pronoun | Despertar | Despertarse |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | me | despierto | me despierto |
| tú | te | despiertas | te despiertas |
| él, ella, usted | se | despierta | se despierta |
| nosotros/as | nos | despertamos | nos despertamos |
| vosotros/as | os | despertáis | os despertáis |
| ellos/as, ustedes | se | despiertan | se despiertan |
Now that you know the Spanish reflexive pronouns and how to conjugate reflexive Spanish verbs, let's take a look at some examples of reflexive verbs in Spanish for describing things that many of us do on a daily basis, with lots of instances from our Yabla video library as always! Here is our list of Spanish reflexive verbs for your daily routine:
The Spanish reflexive verb despertarse means "to wake up":
y por la mañana me despierto entre seis y cuarenta y cinco a siete y cuarto.
and in the morning I wake up between six forty-five and seven fifteen.
Caption 62, Los médicos explican - Diagnóstico: nervios y estrés
Play Caption
After waking up, the next step might be levantarse ("to get up" or "get out of bed"):
Se levanta muy temprano.
She gets up very early.
Caption 51, El Aula Azul - Las Profesiones
Play Caption
In other contexts, the reflexive Spanish verb levantarse could also mean, among other things, "to stand up" or "get up," as from a seat, or even "to rise up against," as in a rebellion.
The Spanish noun baño means "bath," and the verb bañarse can mean "to take a bath" as well. However, as bañarse can also be the more general "to bathe," a person might even use this verb to express the fact that they are taking a shower! Let's look at an example of this reflexive Spanish verb:
Uno se baña todos los días, mijita.
One bathes every day, my girl.
Caption 41, Muñeca Brava - 33 El partido
Play Caption
On the other hand, if a person at the beach expresses their desire to bañarse, rather than wanting to wash the sand off of themselves, they are letting you know they would like to take a dip! The Spanish reflexive verb bañarse can also mean "to go swimming," a translation that often comes as a surprise to English speakers:
No hay muchas olas grandes como en Atacames.
There aren't many big waves like in Atacames.
Es más tranquilo para bañarse.
It's more peaceful to go swimming.
Captions 62-63, Pipo - Un paseo por la playa de Atacames
Play Caption
In the morning, at night, or after the beach, indeed, one might need to ducharse (to take a shower):
¿Qué está haciendo Silvia?
What is Silvia doing?
Silvia se está duchando.
Silvia is taking a shower.
Captions 11-12, El Aula Azul - Actividades diarias: En casa con Silvia
Play Caption
Note that, in this example, the verb ducharse is conjugated in the present progressive tense. As with the present indicative and all other tenses, verbs are conjugated in the exact same way as they would be were they non-reflexive, with the addition of the appropriate reflexive pronoun.
The reflexive verb in Spanish lavarse generally means "to wash (oneself)." Let's look at an example:
Por ejemplo, "Yo me lavo".
For example, "Yo me lavo" [I wash myself].
La acción recae sobre la persona
The action falls back upon the person
que realiza la acción.
who carries out the action.
Pero, "Yo lavo los platos".
But, "Yo lavo los platos" [I wash the dishes].
Captions 45-48, Lecciones con Carolina - Verbos reflexivos
Play Caption
In this informative video about Spanish reflexive verbs, Yabla fan favorite Carolina explains the difference between reflexive and non-reflexive verbs, in this case the verbs lavar (to wash) and lavarse (to wash oneself). Let's look at an additional example:
Yo me lavo las manos. Tú te lavas las manos.
I wash my hands. You wash your hands.
Captions 19-20, Fundamentos del Español - 9 - Verbos Reflexivos
Play Caption
Unlike in English, where we express the idea of washing one's hands or some other body part with a possessive pronoun (my, your, etc.), this is not the case in Spanish. Instead, we use the definite article for the noun in question, manos (hands), in this case, las (the). Because the reflexive pronoun already indicates that the action is something we do to ourselves, it would be redundant in Spanish to say: Yo me lavo mis manos. As the correct way to express this is "Yo me lavo las manos," it might help you to remember the literal but non-sensical translation: "I wash myself the hands."
That said, let's move on to something else that's expressed with the notion of "washing" in Spanish: lavarse los dientes (to brush one's teeth).
Lavarse los dientes (literally "to wash one's teeth") is one of saying "to brush one's teeth" in Spanish:
Después, ehm... suelo lavarme los dientes en el baño,
After that, um... I usually brush my teeth in the bathroom,
Caption 3, El Aula Azul - Actividades Diarias
Play Caption
Different countries, regions, or individuals might instead use cepillarse los dientes, which also means "to brush one's teeth." Let's check out an example in the preterite tense:
Se cepilló los dientes,
He brushed his teeth,
Caption 20, Aprendiendo con Carlos - El microrrelato
Play Caption
By extension, the noun el cepillo means "the brush," and we might have a cepillo de dientes (toothbrush) as well as a cepillo de pelo/cabello (hair brush), as in the following caption:
Sí... -¿Qué necesitamos para ir allí?
Yes... -What do we need to go there?
El cepillo de dientes.
A toothbrush.
El cepillo del pelo.
A hair brush.
Captions 49-51, Un Viaje a Mallorca - Planificando el viaje
Play Caption
So, you've probably surmised by now that the verb cepillarse el pelo/cabello means "to brush one's hair."
The verb peinarse can mean "to comb one's hair" with a comb (un peine), "to brush one's hair," or "to do" or "style" one's hair in general:
Por eso paró en la playa
That's why she stopped on the beach
para mirarse en el espejo y peinarse.
to look at herself in the mirror and comb her hair.
Captions 21-22, Guillermina y Candelario - Mi Amiga la Sirena
Play Caption
Afeitarse is the verb for "to shave" (oneself, of course)!
Vos sabés lo que es todas las mañanas...
Do you know what it's like every morning...
mirarse en el espejo cuando uno se afeita
to look at oneself in the mirror when one's shaving,
Captions 30-31, Muñeca Brava - 8 Trampas
Play Caption
The next step in one's morning routine might be maquillarse (to put on makeup):
Aquí, siempre me maquillo para mis conciertos.
Here, I always put on makeup for my concerts.
Caption 47, Ariana - Mi Casa
Play Caption
Alternatively, one might say Aquí, siempre me pinto para mis conciertos, as pintarse (literally "to paint oneself") also means "to put on makeup."
Vestirse is the way to say "to get dressed" in Spanish.
Yo salgo y... y te vistes.
I'll leave and... and you get dressed.
Caption 30, Confidencial: El rey de la estafa - Capítulo 2
Play Caption
Another way to say this might be ponerse la ropa (to put on one's clothes).
Although sacarse la ropa is one manner of saying "to get undressed" or "take off one's clothes," there are many other examples of reflexive verbs in Spanish that mean the same thing, including: quitarse la ropa, desvestirse, and desnudarse. Let's look at a couple of examples:
Si "Libertinaje" te saca...
If "Libertinaje" takes off your.....
te invita a sacarte la ropa,
invites you to take off your clothes,
Captions 4-5, Bersuit Vergarabat - EPK
Play Caption
Y se desnuda poco a poco y se convierte en tu piel
And she gets naked little by little and she becomes your skin
Caption 6, Reik - Inolvidable
Play Caption
As you can see, the more literal "to get naked" might be an alternate translation for desnudarse.
We're finally getting to the end of our daily routine, when it's time for us to acostarnos (go to bed):
Tranquilícese, vaya a acostarse y deje de pensar en imposibles.
Calm down, go to bed, and stop thinking about impossible things.
Caption 31, Muñeca Brava - 48 - Soluciones
Play Caption
And finally, once in bed, it's time to fall asleep! While the non-reflexive dormir means "to sleep," dormirse means "to fall asleep."
Me dormí pensando en ti; pensando en ti, me desperté
I fell asleep thinking about you; thinking about you, I woke up
Caption 10, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa
Play Caption
Of course, this is just a partial list of reflexive verbs in Spanish that might be applicable to our daily routines. There are a lot more common reflexive verbs in Spanish that describe things one might do on a daily basis, including secarse (to dry oneself off), sentarse (to sit down), sentirse (to feel), emocionarse (to get excited), encontrarse con alguien (to meet with someone), acordarse de (to remember), olvidarse (to forget), sonreírse (to smile), reírse (to laugh), despedirse (to say goodbye), irse (to leave), and many, many more!
For additional information on Spanish reflexive verbs, check out this video from the series Fundamentos del Español. And don't forget to leave us your suggestions and comments.

Let's start today's lesson with a quote from the Argentinean telenovela, Yago:
Pero si no te casás,
But if you don't get married,
no tenés nada para aportar a la sociedad.
you don't have anything to contribute to the company.
No sos nadie, Melina. No sos nada.
You're nobody, Melina. You're nothing.
Captions 27-29, Yago - 9 Recuperación
Play Caption
What's going on here (aside from a seemingly very dramatic situation)? Since the speaker is addressing this character as "you," shouldn't these verbs be conjugated as (tú) te casas, tienes, and eres?
What's going on here, grammatically speaking, is that in Argentina, Uruguay, and many other regions (including parts of Paraguay, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, Mexico, and Venezuela) vos is used in place of tú as the informal second person singular pronoun ("you"), causing some of the verb conjugations to vary slightly.
"Do I really have to learn another verb tense?!" you might be saying. However, even though el voseo (the use of vos instead of tú) might seem intimidating at first, there is a lot of "good news" regarding vos, particularly if you are already familiar with el tuteo (the use of tú):
1. The verb conjugations for vos only differ from those with tú in two tenses: the present indicative and the informal imperative (command). All of the other verb tenses (preterite, imperfect, etc.) are exactly the same as with tú, as are many of its pronouns (e.g. direct object, indirect object, reflexive, and possessive).
2. The formulas for conjugating verbs with vos in both present indicative and imperative are extremely simple.
3. With the voseo, there are a lot less irregular verbs than with tú. In fact, in the present indicative of vos, there are only three irregular verbs, while in the present indicative of tú, there are over one hundred irregular/stem changing verbs to memorize.
Let's start with how to conjugate -ar, -er, and -ir verbs with vos in the present indicative: Simply take the infinitive, replace the "r" with an "s," and add an accent to the final vowel. Let's look at some examples with the infinitives escuchar (to listen), saber (to know), and subir (to go up).
Qu'... Vos no me escuchás ni cuando yo te estoy contando
Wh'... You don't listen to me, not even when I'm telling you
una cosa que para mí es importante.
something that is important to me.
Caption 50, Yago - 2 El puma
Play Caption
Si vos sabés muy bien que yo me sé adaptar.
You know very well that I know how to adapt.
Caption 43, Cuatro Amigas - Piloto
Play Caption
En el segundo piso, de ahí subís y ahí es tu salón.
On the second floor, you go up there and there's your classroom.
Caption 49, La Sucursal del Cielo - Capítulo 1
Play Caption
In the case of these regular -ar and -er verbs, you will note that their conjugations with vos are virtually identical to their tú forms (escuchas and sabes) with the addition of their written (and spoken) accents. However, regular -ir verbs like subir, which are typically conjugated with -es in their tú form (subes), retain their-i vowel plus an accent.
As previously mentioned, verbs that are irregular or stem-changing with tú are regular with vos. To get an idea, let's take the common verbs comenzar (to begin), tener (to have), and decir (to say), all of which have irregular forms when conjugated with tú. With vos, on the other hand, these verbs follow our regular pattern of replacing the "r" with "s" and adding an accent to the final noun:
| Verb in Infinitive: | Present Indicative with Tú: | Present Indicative with Vos: |
|---|---|---|
| comenzar | comienzas | comenzás |
| tener | tienes | tenés |
| decir | dices | decís |
Let's look at a couple of these in action:
Y decís: "Bueno, pará que mañana tenés que seguir."
And you say, "Hey, hold on 'cause tomorrow you have to continue."
Caption 66, Biografía - Natalia Oreiro
Play Caption
There are only three irregular verbs in the vos form of the present indicative, one of which we already saw (ser) and two of which share their forms with tú (haber and ir). All three of these appear in the following clip:
Además, vos ni vas al colegio, has perdido un montón de años.
Besides, you don't even go to school, you have missed a ton of years.
Vos no sos nadie.
You're [a] nobody.
Captions 33-34, La Sucursal del Cielo - Capítulo 1
Play Caption
Now, let's take a look at these captions again, substituting the verb tú for vos:
Además, tú ni vas al colegio, has perdido un montón de años. Tú no eres nadie.
Besides, you don't even go to school, you have missed a ton of years. You're [a] nobody.
While the vos form of ser, sos, does differ from the tú form (eres), the verb conjugations for ir (vas) and haber (has) are exactly the same for both tú and vos.
Conjugating verbs with vos in the imperative (command) form is even easier: Simply take the infinitive, remove the r, and add an accent over the final vowel. Let's look at some examples of the vos command forms for each type of verb ending, utilizing the verbs tomar (to drink), tener (to have), and venir (to come).
Sabés que no tomo whisky. -¡Pero tomá!
You know that I don't drink whiskey. -But, drink it!
Caption 22, Muñeca Brava - 2 Venganza
Play Caption
Este... tené un poquito de paciencia.
Umm... have a little bit of patience.
Caption 7, Muñeca Brava - 45 El secreto
Play Caption
Vení, vamos a bailar.
Come, let's go dance.
Caption 33, Muñeca Brava 7 El poema - Part 6
Play Caption
Once again, verbs like tener and venir that are irregular in the imperative form with tú (ten and ven, respectively) are regular in the imperative form with vos. While ir (to go) is the only irregular verb in this category, its formal conjugations, id or ite, are almost never heard, and the command form of andar (to walk/go), andá, is often used in its place.
Keep in mind that, due to the Spanish accent rules, the addition of a pronoun to a command form with vos may lead to the omission of the written accent:
Olvidate, divertite, hacé algo. -No quiero,
Forget about it, have fun, do something. -I don't want to,
Caption 8, Muñeca Brava 46 Recuperación - Part 7
Play Caption
To conclude, remember that in all of the other tenses besides the present indicative and informal imperative, vos is conjugated in exactly the same way as tú. In the following example, we see the preterite form of ser (to be) fuiste as well as the imperfect form of estar (to be), taking into account that the indirect object pronoun te is also identical for both vos and tú:
Porque a vos no te hice absolutamente nada.
Because I've done absolutely nothing to you.
Todo lo contrario.
On the contrary.
Fuiste la protagonista de la fiesta, estabas maravillosa.
You were the star of the party, you were looking wonderful.
Captions 15-17, Muñeca Brava - 41 La Fiesta
Play Caption
We hope that this lesson has made conjugating verbs with the informal second person pronoun vos seem a bit less daunting. For more information on this topic, we recommend this Yabla series on the Voseo, ustedeo, and tuteo as well as this video on the use of vos in Argentina— and don't hesitate to contact us with your comments and suggestions.
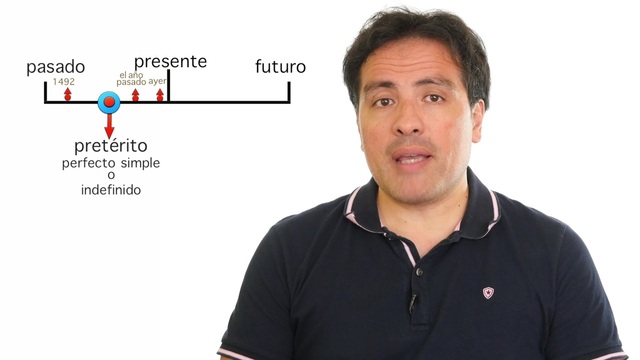
Let's talk about the Spanish conjugation of regular verbs. In particular, let's see how to form the preterite conjugation of regular verbs ending in -ar, -er, and -ir. But first, let's review the main idea behind the preterite tense in Spanish.
In very simple terms, when we talk about the Spanish preterite tense, we are talking about the simple past, in other words, a completed action that took place at a determined point in the past. Let's look at an example from the series where our friend Carlos talks about this tense:
Ayer trabajé hasta las ocho de la noche.
Yesterday I worked until eight at night.
Caption 30, Carlos explica - El pretérito Cap. 1: Perfecto simple o Indefinido
Play Caption
In this example, trabajé is the preterite conjugation of the regular verb trabajar for the first-person singular yo (I). Note that the only change necessary to form the preterite in this example is removing the -ar ending of the infinitive verb and replacing it with the ending -é.
There are a couple of things we want to mention about the conjugations you will find throughout this tutorial.
1. While usted (the formal, second-person singular "you") does not appear in our conjugation lists, keep in mind that when using that pronoun, the verb is conjugated in the exact same way as verbs in the third-person singular forms with él (he) and ella (she). Let's take a look at this in action with the preterite conjugation of the verb hablar (to speak/talk):
Usted habló de Fabio Sirenio.
You talked about Fabio Sirenio.
Caption 83, Yago - 7 Encuentros - Part 14
Play Caption
Entonces él habló con...
So, he spoke with...
con los pescadores y los pescadores aceptaron.
with the fishermen and the fishermen accepted.
Caption 17, Instinto de conservación - Parque Tayrona
Play Caption
2. In order to offer a more simplistic verb conjugation snapshot, in this article, we only employ the masculine versions of the plural forms nosotros (we), vosotros (you), and ellos (they). That said, keep in mind that the conjugations are the same for the feminine forms nosotras, vosotras, and ellas.
3. Just like usted, ustedes (the standard second person plural "you" in Latin America and the formal second person plural in Spain) does not appear among the conjugations shared here. However, keep in mind that the conjugations of verbs with "ustedes" are the exact same as the third-person plural forms utilized with ellos and ellas (they). Let's look at an example of this with the preterite conjugation of the verb cantar (to sing):
Ustedes cantaron muy bien (You guys sang very well).
Ellos/Ellas cantaron muy bien (They sang very well).
Having said all this, let's explore the preterite conjugations of some regular verbs in Spanish.
Let's take a look at the preterite conjugation of the verb hablar (to speak).
Yo hablé (I spoke).
Tú hablaste (You spoke).
Él/Ella habló (He/She spoke).
Nosotros hablamos (We spoke).*
Vosotros hablasteis (You spoke).
Ellos hablaron (They spoke).
* It's important to note that because the verb conjugation for the first person plural "nosotros" (we) is the same for both the simple present and simple past tenses, the speaker's intention must be determined by context as follows:
Nosotros estudiamos mucho todos los días (We study a lot every day).
Ayer nosotros estudiamos mucho (Yesterday, we studied a lot).
Example 1.: The verb comprar (to buy)
¡Y compraste melones en vez de limones!*
And you bought melons instead of lemons!
Caption 16, Extr@: Extra en español - Ep. 2: Sam va de compras
Play Caption
* Remember that pronouns are frequently omitted in Spanish. Thus, in the example above and without changing the meaning, one could say: "¡Y tú compraste melones en vez de limones!" However, despite the fact that the speaker does not use the pronoun here, the -aste verb ending lets the listener know that the person referred to is "tú" (you).
Example 2.: The verb escuchar (to listen/hear)
La canción que escuchamos
The song that we heard
introduce la quinta parte del primer episodio.
introduces the fifth part of the first episode.
Caption 54, Carlos comenta - Los Años Maravillosos - La década de los 80 y música
Play Caption
Let's take a look at the preterite conjugation of the regular verb comer (to eat).
Yo comí (I ate).
Tú comiste (You ate).
Él/Ella comió (He/She ate).
Nosotros comimos (We ate).
Vosotros comisteis (You ate).
Ellos comieron (They ate).
Example 1.: The verb aprender (to learn)
...y aprendí que los pulpos pueden cambiar de color.
...and I learned that octopi can change color.
Caption 45, Guillermina y Candelario - La Señora Pulpo
Play Caption
Example 2.: The verb vender (to sell)
Creo que vendimos unos quinientos dólares en unas...
I think we sold about five hundred dollars (worth) in about...
tres horas, dos horas.
three hours, two hours.
Captions 25-26, Un café con Julia - Año nuevo
Play Caption
Let's take a look at the preterite conjugation of the verb vivir (to live).
Yo viví (I lived).
Tú viviste (You lived).
Él/Ella vivió (He/She lived).
Nosotros vivimos (We lived).
Vosotros vivisteis (You lived).
Ellos vivieron (They lived).
Example 1.: The verb escribir (to write)
¿Por qué dices eso?
Why do you say that?
Porque una vez me escribiste
Because once you wrote to me
contándome que te casabas en Nueva York.
telling me that you were getting married in New York.
Captions 61-62, Yago - 6 Mentiras - Part 5
Play Caption
Example 2.: The verb abrir (to open)
Primero, Lisa Bernal abrió la herida.
First, Lisa Bernal opened the wound.
Caption 61, Los Años Maravillosos - Capítulo 6 - Part 4
Play Caption
And with this example, we have reached the end of this lesson. But before we go, a little homework for you: go ahead and choose some other regular verbs and practice the Spanish conjugation of the preterite tense. Sooner or later, you will be able to master those preterite endings! We hope you enjoyed this lesson, and don't forget to leave us your comments and suggestions. ¡Hasta la próxima!

Today's lesson will examine Yabla's "Top 12" picks for the most useful verbs for having a conversation in Spanish. This time, we'll focus on the meanings of those verbs as well as giving you a lot of simple, conversational examples from Yabla's Spanish video library. Additionally, we'll provide you with conjugation tables for the "Top 3" most useful Spanish tenses: the simple present, the imperfect (which describes ongoing or continuous past actions), and the preterite (which describes completed past actions).
In addition to the aforementioned links, you can consult this lesson entitled Spanish Verb Tenses Explained if you need to brush up on those tenses and more! Although memorizing all of these conjugations might seem a bit intimidating, it could really help your ability to converse in Spanish.
The fact that there are two verbs that mean "to be" in Spanish, ser and estar, can feel quite confusing for non-native speakers. Generally speaking, the verb ser is employed to describe more permanent characteristics. The acronym DOCTOR (description, occupation, condition, time, origin, relationship) is very useful for helping us to remember some of the many situations in which this verb is used. Let's take a look at how this verb is conjugated as well as some examples:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | soy | era | fui |
| Tú | eres | eras | fuiste |
| Él, ella, usted | es | era | fue |
| Nosotros, nosotras | somos | éramos | fuimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | sois | erais | fuisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | son | eran | fueron |
Soy profesor de fotografía.
I'm a photography teacher.
Caption 13, 75 minutos - Gangas para ricos - Part 5
Play Caption
Sus cuadros eran muy extraños.
His paintings were very strange.
Caption 25, El Aula Azul - Adivina personajes históricos
Play Caption
También fuimos parte de todas estas, eh... mega empresas, pero...
We were also part of all these, um... mega companies, but...
Caption 22, Doctor Krápula - Entrevista
Play Caption
Notably, although ser usually denotes permanence, while the preterite tense denotes that something had a definite ending point, the verb ser is used in the preterite to describe something that "was" in the past, but did come to a conclusive end.
The verb estar also means "to be" for traits that are variable/less permanent. The acronym PLACE (position, location, action, condition, emotion) might help you to remember some contexts in which the verb estar should be chosen. Let's take a look:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | estoy | estaba | estuve |
| Tú | estás | estabas | estuviste |
| Él, ella, usted | está | estaba | estuvo |
| Nosotros, nosotras | estamos | estábamos | estuvimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | estáis | estabais | estuvisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | están | estaban | estuverion |
Sí... Vale, entonces, estamos aquí.
Yes... OK, then, we're here.
Caption 6, Curso de español - Disculpe, ¿hay un cine por aquí?
Play Caption
Un poquito y ajá, y estaba triste porque
A little bit, and uh-huh, and I was sad because
dejaba mi familia y eso y ya.
I was leaving my family and all that and that's it.
Caption 70, Cleer - Entrevista a Lila
Play Caption
Los árabes estuvieron en España más de seiscientos años.
The Arabs were in Spain for more than six hundred years.
Caption 23, Rosa - Antequera, Málaga
Play Caption
Be sure to check out this lesson if you want to learn more about the difference between ser and estar.
The verb tener means "to have" in Spanish. Let's take a closer look:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | tengo | tenía | tuve |
| Tú | tienes | tenías | tuviste |
| Él, ella, usted | tiene | tenía | tuvo |
| Nosotros, nosotras | tenemos | teníamos | tuvimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | tenéis | teníais | tuvisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | tienen | tenían | tuvieron |
¿Tienes plumones y tijeras?
You have markers and scissors?
Sí, tengo plumones y tijeras,
Yes, I have markers and scissors,
pero no tengo mi teléfono.
but I don't have my phone.
Captions 20-22, Conversaciones en el parque - Cap. 1: No tengo mi teléfono.
Play Caption
Tenían mi mochila en la Oficina de Objetos Perdidos.
They had my backpack in the Lost and Found.
Caption 44, Raquel - Oficina de objetos perdidos
Play Caption
La noche anterior a la rumba, tuve otro sueño.
The night before going out on the town, I had another dream.
Caption 1, Los Años Maravillosos - Capítulo 7
Play Caption
Additionally, we invite you to explore some of the many idiomatic expressions with the verb tener.
And, we'll just take a second to mention that if you throw in the word que after the verb tener plus a verb's infinitive ("to" form), you'll have the very useful Spanish construction tener que that means, "to have to" (do something):
Hoy tengo que trabajar.
Today I have to work.
Caption 74, 75 minutos - Gangas para ricos - Part 14
Play Caption
Tuvimos que trasladarnos a esta nueva ciudad.
We had to move to this new city.
Caption 39, Ciudad de Panamá - Denisse introduce la ciudad
Play Caption
The Spanish verb hacer can mean either "to make" or "to do." But, not to fear— typically, the context will let you know quite clearly which meaning is intended.
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | hago | hacía | hice |
| Tú | haces | hacías | hiciste |
| Él, ella, usted | hace | hacía | hizo |
| Nosotros, nosotras | hacemos | hacíamos | hicimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | hacéis | hacíais | hicisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | hacen | hacían | hicieron |
Y ¿tú qué haces?
And what are you doing?
Caption 24, Guillermina y Candelario - Un pez mágico
Play Caption
Y yo no hacía esto. Yo hago otro acto, que es con las motos.
And I didn't do this. I do another act, which is with motorcycles.
Caption 35, Rueda de la muerte - Parte 1
Play Caption
También hizo alguna película.
He also made a movie.
Caption 28, El Aula Azul - Adivina personajes históricos
Play Caption
The Spanish verb ir means "to go." Let's check out some of its conjugations and uses:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | voy | iba | fui |
| Tú | vas | ibas | fuiste |
| Él, ella, usted | va | iba | fue |
| Nosotros, nosotras | vamos | íbamos | fuimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | vais | ibais | fuisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | van | iban | fueron |
Voy a la piscina los lunes y los miércoles.
I go to the pool on Mondays and Wednesdays.
Caption 7, Ariana - Mi Semana
Play Caption
Iba mucho con mi padre al campo.
I used to go with my father to the countryside a lot.
Caption 56, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa - Part 10
Play Caption
¿Por qué fuiste al cine?
Why did you go to the movies?
Caption 48, Carlos explica - Las preposiciones 'por' y 'para'
Play Caption
You might have noticed that the preterite form of the verb ir is conjugated in the exact same way as the verb ser. However, in most cases, context should help you to easily identify which verb is in use.
Another great "trick" to be aware of is that adding an a plus a verb's infinitive to the verb ir is a very simple way of expressing what we are "going to" do and is, thus, an alternative to the future tense. Let's take a look:
Vamos a hablar de mi familia, ¿sí?
We are going to talk about my family, OK?
Caption 2, Curso de español - Vamos a hablar de la familia
Play Caption
Porque las chicas iban a salir, para no dejarte sola.
Because the girls were going to go out, so you wouldn't be alone.
Caption 11, Muñeca Brava - 18 - La Apuesta
Play Caption
If we're going to talk about ir (to go), we'd better mention venir (to come)! Let's look:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | vengo | venía | vine |
| Tú | vienes | venías | viniste |
| Él, ella, usted | viene | venía | vino |
| Nosotros, nosotras | venimos | veníamos | vinimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | venís | veníais | vinisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | vienen | venían | vinieron |
Yo vengo del sur de España
I come from the South of Spain
Caption 10, Carolina - Acentos
Play Caption
¿Qué venía después?
What came next?
Caption 23, Los Años Maravillosos - Capítulo 8
Play Caption
Los otros cisnes vinieron hacia él.
The other swans came toward him.
Caption 50, Cleer - El patito feo
Play Caption
The Spanish verb decir means "to say" or "to tell."
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | digo | decía | dije |
| Tú | dices | decías | dijiste |
| Él, ella, usted | dice | decía | dijo |
| Nosotros, nosotras | decimos | decíamos | dijimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | decís | decíais | dijisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | dicen | decían | dijeron |
Yo digo que Playa Balandra es el paraíso oficial.
I say that Balandra Beach is the official paradise.
Caption 67, Alan x el mundo - Mi playa favorita de México!
Play Caption
Pero siempre me decía: ¡Mira! Mira eso allá.
But he always used to tell me: Look! Look at that over there.
Caption 42, Federico Kauffman Doig - Arqueólogo
Play Caption
Y la señorita me dijo algo completamente diferente.
And the lady told me something totally different.
Caption 45, Confidencial: El rey de la estafa - Capítulo 5
Play Caption
Since we often say or tell things "to" others, you will notice that the verb decir is quite typically accompanied by indirect object pronouns like me (to me), te (to you), etc. to indicate the person to whom something is said or told. You can learn more about this and other aspects of this verb in our lesson entitled The Spanish Verb Decir.
The verb poder means "to be able." It can be used alone to say simply "I can," "you could," etc. but is often used in conjunction with an infinitive verb to express what it is one "is able" to do. Let see it in action:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | puedo | podía | pude |
| Tú | puedes | podías | pudiste |
| Él, ella, usted | puede | podía | pudo |
| Nosotros, nosotras | podemos | podíamos | pudimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | podéis | podíais | pudisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | pueden | podían | pudieron |
¿Puedo ver el menú por favor?
Can I see the menu please?
Caption 12, Cata y Cleer - En el restaurante
Play Caption
¿Por qué las cosas no podían ser sencillas?
Why couldn't things be easy?
Caption 31, Los Años Maravillosos - Capítulo 10
Play Caption
Gracias a su cola, pudieron volar.
Thanks to its tail, you were able to fly.
Caption 49, Guillermina y Candelario - Una aventura extrema
Play Caption
To learn more about the verb poder and how it is used, we recommend the following lesson: The Verb Poder - Common Expressions.
This word means "to know," but, in its preterite form, can mean "to find out."
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | sé | sabía | supe |
| Tú | sabes | sabías | supiste |
| Él, ella, usted | sabe | sabía | supo |
| Nosotros, nosotras | sabemos | sabíamos | supimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | sabéis | sabíais | supisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | saben | sabían | supieron |
Pero no sé dónde!
But I don't know where!
Caption 28, NPS No puede ser - 1 - El concurso
Play Caption
No sabía qué decirle.
I didn't know what to say to her.
Caption 12, Los Años Maravillosos - Capítulo 1
Play Caption
Nunca supe la verdad
I never found out the truth
Caption 2, Aleks Syntek - Intocable
Play Caption
If we're going to converse in Spanish, we had better be able to say what we "want"! The verb querer can stand alone to express our desire for a particular thing or be used with an infinitive verb to say what we "want to do." Let's take a look:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | quiero | quería | quise |
| Tú | quieres | querías | quisiste |
| Él, ella, usted | quiere | quería | quiso |
| Nosotros, nosotras | queremos | queríamos | quisimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | queréis | queríais | quisisteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | quieren | querían | quisieron |
Porque realmente quiero mi propio baño.
Because I really want my own bathroom.
Caption 37, Cleer y Lida - Reservando una habitación
Play Caption
Y algunos querían volver a su casa.
And some wanted to go back to their home.
Caption 13, Guillermina y Candelario - El mundo de los juguetes perdidos
Play Caption
No me quiso decir su nombre.
She wouldn't tell me her name.
Caption 8, Yago - 14 La peruana
Play Caption
Keep in mind that when the verb querer is used with no in the preterite, it can convey the idea that someone "wouldn't" do something or "refused to."
One more important aspect of the Spanish verb querer is that, when speaking about actions that we "want" others to do or that we "want" to happen, the subjunctive form of the verb that follows is required (vuelvas instead of vuelves in the following example):
Quiero que... que vuelvas a New York.
I want for... for you to come back to New York.
Caption 23, Yago - 11 Prisión
Play Caption
The Spanish verb dar means "to give." Let's look at some of its forms and examples:
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | doy | daba | di |
| Tú | das | dabas | diste |
| Él, ella, usted | da | daba | dio |
| Nosotros, nosotras | damos | dábamos | dimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | dais | dabais | disteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | dan | daban | dieron |
Yo doy agua a mi gato.
I give water to my cat.
Caption 14, Lecciones con Carolina - Verbo - dar
Play Caption
Adriana Espinel siempre daba unas respuestas tan profundas.
Adriana Espinel always gave such deep answers.
Caption 72, Los Años Maravillosos - Capítulo 4
Play Caption
Eh... Mi asistente me dio sus datos.
Um... My assistant gave me your information.
Caption 39, Confidencial: El rey de la estafa - Capítulo 1
Play Caption
Like the verb decir, the verb dar is often accompanied by indirect object pronouns to highlight the person to whom something is given.
And, to conclude our list of the Top 12 Spanish verbs for carrying on a conversation, we thought it would be a good idea to give you a verb to describe the things you observe!
| Personal Pronoun | Present | Imperfect | Preterite |
| Yo | veo | veía | vi |
| Tú | ves | veías | viste |
| Él, ella, usted | ve | veía | vio |
| Nosotros, nosotras | vemos | veíamos | vimos |
| Vosotros, vosotras | veis | veíais | visteis |
| Ellos, ellas, ustedes | ven | veían | vieron |
Eh... ¿Cómo veo la vida?
Um... How do I see life?
Caption 79, Adícora, Venezuela - El tatuaje de Rosana
Play Caption
¡Pero veíamos serpientes por todos lados!
But we saw snakes everywhere!
Caption 41, Guillermina y Candelario - La Isla de las Serpientes
Play Caption
Vimos una película.
We saw a movie.
Caption 14, Zulbani - Trip to Merida
Play Caption
Although it was certainly tough to narrow down the top 12 useful verbs in Spanish for carrying on a conversation, we hope you've enjoyed this lesson and that it helps you to hold a lot of stimulating conversations! Let us know with your suggestions and comments if there are any other verbs or topics you'd like to learn more about.

Generally speaking, we use the conditional tense in Spanish to talk about hypothetical things. However, we also use the conditional tense for polite requests or when we want to express wishes and desires. Let's take a look at some simple rules that will help you to master the conditional tense in Spanish.
Before talking about the uses of the conditinal tense, it is important to review how to conjugate it. Let's start with the regular verbs. For these verbs, you just need to take the infinitive form and add the conditional ending.
Let's take the verb hablar (to speak)
Yo hablaría (I would speak)
Tú hablarías (You would speak)
Él/Ella hablaría (He/She would speak)
Nosotros hablaríamos (We would speak)
Vosotros hablaríais (You would speak)
Ellos hablarían (They would speak)
Let's take the verb comer (to eat)
Yo comería (I would eat)
Tú comerías (You would eat)
Él/Ella comería (He/She would eat)
Nosotros comeríamos (We would eat)
Vosotros comeríais (You would eat)
Ellos comerían (They would eat)
Let's take the verb abrir (to open)
Yo abriría (I would open)
Tú abrirías (You would open)
Él/Ella abriría (He/She would open)
Nosotros abriríamos (We would open)
Vosotros abriríais (You would open)
Ellos abrirían (They would open)
There are several irregular verbs that are used all the time in the conditional tense. For these verbs, you need to keep in mind that they maintain the same stem that they have in the future tense. Let's see the conjugation for the verbs decir (to say) and hacer (to make).
Yo diría (I would say)
Tú dirías (You would say)
Él/Ella diría (He/She would say)
Nosotros diríamos (We would say)
Vosotros diríais (You would say)
Ellos dirían (They would say)
Yo haría (I would make)
Tú harías (You would make)
Él/Ella haría (He/She would make)
Nosotros haríamos (We would make)
Vosotros haríais (You would make)
Ellos harían (They would make)
In Spanish, it is quite common to use the conditional tense when you want to do any of the following:
¿Podrías por favor decirnos a los... a nuestros amigos de Yabla
Could you please tell us to the... to our friends from Yabla
en qué lugar están ustedes?
where you guys are?
Captions 66-67, Monsieur Periné - Entrevista
Play Caption
¿Te gustaría volver a tu ciudad?
Would you like to return to your city?
Pues la verdad es que me encantaría volver a Málaga.
Well the truth is that I would love to go back to Málaga.
Captions 33-34, Clara y Cristina - Saludar
Play Caption
Bueno, si yo fuera tú, hablaría con él.
Well, if I were you, I would speak with him.
Caption 24, El Aula Azul - La Doctora Consejos: Subjuntivo y condicional
Play Caption
Cuatro horas es demasiado.
Four hours is too much.
Creo que no llegaría a tiempo a la reunión.
I think that I would not arrive in time for the meeting.
Captions 30-31, Raquel - La Compra de un Billete de Tren
Play Caption
Y que nos juramos que esto nunca iría a pasar
And we vowed to each other that this would never happen
Caption 21, Franco de Vita, Dueto Con Debi Nova - Si Quieres Decir Adiós
Play Caption
That's it for this lesson. We encourage you to write some sentences for the 5 different uses we mentioned for the conditional tense. And don't forget to send us your feedback and suggestions.

How many regular '-ir' verbs do you know in Spanish? Now that we have already talked about verbs ending in ‘-ar’ and verbs ending in '-er', it's time to take a look at the last main group of regular verbs. Again, keep in mind that we form regular verbs when we put together a verb stem and an infinitive ending. For example, the verb describir (to describe) is made with the verb stem 'describ' plus the infinitive ending '-ir'. With that being said, let's take a look at the following regular verbs ending in '-ir':
We know we have a regular verb when the verb stem doesn't change once it is conjugated. Do you want to see how that works in the simple present? Let’s use the verb abrir (to open) for this:
Abres el rombo, y el pico superior lo doblas hacia abajo.
You open the diamond, and the top point you fold downwards.
Captions 46-47, Manos a la obra - Separadores de libros: Charmander
Play Caption
Now, let’s see how to conjugate a regular '-ir' verb in the simple past. Let's take the verb escribir (to write):
Gabriel García Márquez escribió muchos libros.
Gabriel Garcia Marquez wrote a lot of books.
Caption 50, Carlos explica - El pretérito Cap. 1: Perfecto simple o Indefinido
Play Caption
It is worth noting that for the first person plural (nosotros), the conjugation of the verb is exactly the same in both the simple present and the simple past:
...pero cuando escribimos estas dos palabras.
...but when we write these two words.
Caption 45, Lecciones con Carolina - Haber vs. A Ver / Si vs. Sí
Play Caption
Now, let’s take one of the most common verbs in Spanish in order to see the conjugation of a regular ‘ir’ verb in the simple future:
...y que viviremos en un hogar agradable.
...and that we will live in a nice home.
Caption 55, Negocios - La solicitud de empleo
Play Caption
Unlike the simple present and past, the conjugation in the simple future leaves the verb as it is (vivir) only adding a different ending.
Let’s learn some more regular -ir verbs with the following sentences:
1. Aplaudir (to clap)
...o por ejemplo, en el flamenco se aplaude así.
...or for example, in flamenco one claps like this.
Caption 46, Marta de Madrid - El cuerpo - El tronco
Play Caption
2. Decidir (to decide)
De un momento a otro, decidió quedarse en Bogotá.
From one minute to another, she decided to stay in Bogota.
Caption 22, Confidencial: El rey de la estafa - Capitulo 4
Play Caption
3. Discutir (to discuss/argue)
Chica, sabes que yo no discuto con novatas después del mediodía.
Girl, you know that I don't argue with rookies after noon.
Caption 57, NPS No puede ser - 1 - El concurso
Play Caption
4. Subir (to climb/go up/increase)
Subimos la temperatura del depósito a ochenta grados.
We increase the temperature of the tank to eighty degrees.
Caption 25, Club de las ideas - Biodiesel
Play Caption
5. Sufrir (to suffer)
Sufres, gritas, nadie te da nada
You suffer, you scream, nobody gives you anything
Caption 21, Club de las ideas - La motivación
Play Caption
That’s it for this lesson. Now that we have covered all the three groups of regular verbs, go ahead and try to write some sentences with verbs ending in -ar, -er and -ir. And don’t forget to send us your feedback and suggestions.

Let’s talk about verbs. As we mentioned before, in Spanish language, all regular verbs belong to one of the following groups: verbs ending in ‘-ar’, verbs ending in ‘-er’ and verbs ending in ‘-ir’. Today, we will take a look at those verbs ending in ‘-er’.
Before that, however, let’s keep in mind that regular verbs are formed using the following formula: verb stem + infinitive ending. Let’s look at some of the most common regular ‘ER’ verbs in Spanish:
A verb is considered regular when the verb stem doesn’t change from the infinitive form to the conjugated form of the verb. Let’s take the regular verb aprender (to learn) and see its conjugation in the simple present. Notice how the stem stays the same but the endings vary:
Aquí aprenden a diseñar y confeccionar decorados.
Here they learn to design and make decorations.
Caption 26, Europa Abierta - Taller de escenografía en Olivares
Play Caption
Now, let’s take the regular verb comer (to eat) and see how the conjugation works in the simple past:
Fuimos a pasear, comimos un helado.
We went for a walk, we ate an ice cream.
Caption 29, El Aula Azul - La Doctora Consejos - El pasado
Play Caption
Let’s use a different verb to see the conjugation of a regular ‘er’ verb in the simple future. Let’s take the verb vender (to sell):
Mañana venderé mi casa.
Tomorrow, I will sell my house.
Let’s finish this lesson by learning more verbs with these 5 sentences using er verbs in Spanish:
1. Beber (to drink)
Yo bebo agua.
I drink water.
Caption 27, El Aula Azul - Actividades diarias - En casa con Silvia
Play Caption
2. Comprender (to comprehend / understand)
Ahora comprendo mejor la operación de mi padre.
Now I understand my father's operation better.
Caption 65, Club de las ideas - Lego Fest en Sevilla
Play Caption
3. Correr (to run)
Corrió hacia la puerta y cuando el príncipe trató de seguirla...
She ran to the door and when the prince tried to follow her...
Caption 16, Cuentos de hadas - La Cenicienta
Play Caption
4. Prometer (to promise)
Ayer os prometí que estudiaríamos hoy "aconsejar,"
Yesterday I promised you that today we would learn "to advise,"
Caption 1, Escuela Don Quijote - En el aul
Play Caption
5. Temer (to fear / be afraid of)
Pero ellos no le temen a nada.
But they are not afraid of anything.
Caption 23, Salvando el planeta Palabra - Llegada
Play Caption
That’s it for this lesson. Now, a final challenge: Take one of the sentences we just mentioned and try to change it using a different person and a different verb tense. And don’t forget to send your feedback and suggestions.

In the Spanish language, all infinitive verbs belong to one of the following groups: verbs ending in ‘-ar’, verbs ending in ‘-er’ and verbs ending in ‘-ir’.
Likewise, each infinitive verb is formed using the following formula:
Verb stem + infinitive ending.
Let’s look at some of the most common regular ‘AR’ verbs in Spanish:
Hablar (to speak) = Habl + ar
Comprar (to buy) = Compr + ar
Estudiar (to study) = Estudi + ar
A verb is considered regular when the verb stem doesn’t change from the infinitive form to the conjugated form of the verb. Let’s take the regular verb hablar (to speak) and see its conjugation in the simple present. Notice how the stem stays the same but the endings vary:
Yo hablo (I speak)
Tú hablas (You speak)
Él/Ella habla (He/She speaks)
Nosotros/as hablamos (We speak)
Vosotros/as habláis (You speak)
Ellos/as hablan (They speak)
... o cuando mis alumnos hablan español.
... or when my students speak Spanish.
Caption 84, Lecciones con Carolina - Adjetivos posesivos
Play Caption
Now, let’s take the regular verb comprar (to buy) and see how the conjugation works in the simple past:
Yo compré (I bought)
Tú compraste (You bought)
Él/Ella compró (He/She bought)
Nosotros/as compramos (We bought)
Vosotros/as comprasteis (You bought)
Ellos/as compraron (They bought)
¿Recuerdas el regalo que compré? -Mm-hm.
Do you remember the gift that I bought? -Mm-hm.
Caption 17, El Aula Azul - La Doctora Consejos - El pasado
Play Caption
Let’s use a different verb to see the conjugation of a regular ‘AR’ verb in the simple future. Let’s take the verb estudiar (to study):
Yo estudiaré (I will study)
Tú estudiarás (You will study)
Él/Ella estudiará (He/She will study)
Nosotros/as estudiaremos (We will study)
Vosotros/as estudiaréis (You will study)
Ellos/as estudiarán (They will study)
La Comisaría de Pesca dice que estudiará la forma de pagar esa indemnización.
The Fisheries Commissioner says that she will evaluate the way to pay that compensation.
Caption 50, Europa Abierta - Aguas en discordia
Play Caption
Take a look at the following list featuring some of the most used 'AR' verbs in Spanish:
Ahora puedo cantar.
Now I can sing.
Caption 36, Ariana Cita médica
Play Caption
nos gusta bailar, nos gusta disfrutar,
we like to dance, we like to have fun,
Caption 34, Días festivos La diablada pillareña - Part 1
Play Caption
In this example, the speaker also uses another -ar verb in Spanish: disfrutar (to have fun/to enjoy).
Y ahora, voy a bajar.
And now, I am going to go down.
Caption 15, Raquel Las direcciones
Play Caption
Comenzó a caminar sin rumbo fijo.
He began to walk with no particular destination in mind.
Caption 39, Aprendiendo con Carlos El microrrelato - Part 2
Play Caption
Tengo que contestar esta llamada.
I have to answer this call.
Caption 9, Confidencial: El rey de la estafa Capítulo 3 - Part 1
Play Caption
Me encanta descansar un poquito después del trabajo.
I love to rest a little bit after work.
Caption 21, Ariana Mi Casa
Play Caption
para entrar en nuevos mercados.
to enter into new markets.
Caption 6, Negocios Problemas laborales - Part 1
Play Caption
Tómate un tiempo para escuchar,
Take some time to listen to,
Caption 17, Ana Carolina Mejorando la pronunciación
Play Caption
Ahora sólo me falta limpiar mi mesa de noche.
Now I just have to clean my nightstand.
Caption 27, Ana Carolina Arreglando el dormitorio
Play Caption
Now, a final challenge: take one of the verbs we just mentioned and try conjugating it in simple present, past and future. And don’t forget to send your feedback and suggestions.
Spanish Reflexive Verbs for Your Daily Routine

Let's talk about pronouns. In English, when we talk with someone we use the second person singular pronoun ‘you’. In Spanish, we have three different options for that same pronoun: tú, usted and vos. Which one we use depends on things like the relationship that we have with the person we are talking to or the place where we are. Generally speaking, we use usted when we want to talk in a more respectful way with someone:
¿Usted qué... qué me recomienda, doctor?
What do you... what do you recommend to me, Doctor?
Caption 14, Los médicos explican - El tratamiento de las fracturas
Play Caption
However, if you are following the Colombian series Los Años Maravillosos, you have probably noticed that people usually use usted even when talking with family members or close friends. Why? That’s just how people speak in Bogota, Colombia:
¿Y a usted qué le pasa, mi hijito?
And what's going on with you, my little boy?
Caption 35, Los Años Maravillosos - Capítulo 1
Play Caption
Regardless of its use, there is something quite unique about using usted: we conjugate usted as we would conjugate él (he) or ella (she):
Él trabaja entre las nueve de la mañana
He works between nine in the morning
Caption 48, La casa - De Chus
Play Caption
¿Dónde trabaja usted?
Where do you work?
Caption 9, 75 minutos - Gangas para ricos
Play Caption
As you can see in the captions above, the conjugation of the verb trabajar (to work) with él (he) and usted (you) is exactly the same (trabaja), something that doesn’t occur with tú and vos:
Tú trabajas | You work
Vos trabajás | You work
Él/Ella/Usted Trabaja | He/She/You work
To wrap things up, we use usted as a second person singular pronoun. However, we conjugate it as a third person singular pronoun!
And don’t forget that this also occurs with the plural form ustedes (you all), which we conjugate as the third person plural pronoun ellos/ellas (they). Notice how ustedes and ellos share the same conjugation of the verb saber (to know) in the following captions:
Toda la vida he estado en el PAN, como ustedes saben, y he estado muy contento.
All my life I have been in PAN, as you know, and I have been very happy.
Caption 37, Felipe Calderón - Publicidad
Play Caption
Ellos saben de los sitios que son hábitat de reproducción,
They know about the places that are reproduction habitats,
Caption 31, Instinto de conservación - Parque Tayrona
Play Caption
That's it for now. If you want to learn more things about the use of tú, usted, and vos, make sure to check out our series about Tuteo, Ustedeo y Voseo. And don’t forget to send us your feedback and suggestions.

We all know that mastering irregular verbs like ser (to be) and ir (to go) can be tricky. Very often, however, we can take advantage of those special rules that make the learning process a bit easier. In this lesson, we will explore one of them: the ser and ir preterite conjugation!
First of all, the good news: the verbs ser and ir share the same simple past conjugation! By simple past, we are referring to what is known in Spanish as pretérito perfecto simple or just pretérito (preterite). That being said, let’s review the ser and ir preterite conjugation of these two verbs.
Yo fui | I was
Tú fuiste | You were
Él/Ella fue | He/She was
Nosotros fuimos | We were
Vosotros fuisteis | You were
Ellos fueron | They were
Let's see a couple of examples:
Pensar que un día fui la respuesta
To think that one day I was the answer
Caption 15, Belanova - Tal vez
Play Caption
Aprendí que los primeros en hacer cómic fueron los aztecas.
I learned that the first ones to make comics were the Aztecs.
Captions 47-48, Antonio Vargas - Artista - Comic
Play Caption
Yo fui | I went
Tú fuiste | You went
Él/Ella fue | He/She went
Nosotros fuimos | We went
Vosotros fuisteis | You went
Ellos fueron | They went
Did you see that? The ser and ir preterite conjugation is the same! Now, let's see a couple of examples with the verb ir:
Y sí, definitivamente fuimos a tomar un café, fuimos a cenar.
And yes, we definitely went for a coffee, went to dinner.
Caption 18, Enanitos Verdes - Luz de día
Play Caption
¿Y te fuiste a vivir con tu novio con cuánto?
And you went to live with your boyfriend when you were how old?
-Con diecisiete.
-I was seventeen.
Caption 92, 75 minutos - Gangas para ricos - Part 14
Play Caption
We also use the simple past conjugation of the verb ir for the reflexive form irse (to leave):
Yo me fui de la casa cuando tenía nueve años.
I left home when I was nine years old.
Caption 41, La Sub30 - Familias - Part 5
Play Caption
Desde aquel día que te fuiste, supe que eras para mí
From that day on which you left, I knew you were for me
Caption 1, Andy Andy - Maldito Amor
Play Caption
That's all for now. But before we leave, a short exercise for you: Write 10 sentences using the preterite of the verb ser and 10 sentences using the preterite of the verb ir. and don't forget to leave us your suggestions and comments.

The verb decir (to say, to tell) is very common in Spanish. Let’s learn how to use it.
One of the most commonly used forms of this verb is digo (I say):
Pero si yo digo: Yo voy en el autobús y usted va en el coche,
But if I say: I am going in the bus and you [formal] are going on the car,
Captions 49-51, Fundamentos del Español - 6 - Tú y Usted
Play Caption
The verb decir is frequently followed by the word que (that):
Yo digo que la fruta es para comerla no para hacerse una fotografía con ella.
I say that fruit is to eat it not to take a picture with it.
Caption 48, Los Reporteros - Sembrar, comer, tirar - Part 2
Play Caption
Also remember that in Spanish you don't always need to use personal pronouns before verbs, since these are conjugated differently for each person:
Pues entonces rejuvenece coger castañas. -Digo que sí.
Well then, it rejuvenates to pick chestnuts. -I say so.
Captions 18-19, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa - Part 4
Play Caption
Another common instance of the verb decir is dice (he/she/it says). The reason why dice is very useful is because it helps us talk about what we read or hear. For example:
Hay un letrero en la puerta que dice que ya está cerrado | There's a sign on the door sayingit's closed already.
El mensaje dice que viene una gran tormenta | The message says a big storm is coming.
Mayra dice que te tienes que ir | Mayra says you have to go.
We mentioned before that it’s very common to omit personal pronouns before verbs in Spanish. But you will find that the verb decir is frequently preceded by reflexive, direct, or indirect object pronouns (me, te, se, nos, os, le, les, la, las, lo) depending on what is being said and to whom. For example:
¿Quién nos dice que la vida nos dará el tiempo necesario?
Who says [to us] life will give us the necessary time?
Caption 11, Julieta Venegas - El Presente
Play Caption
Supongamos que un amigo me dice lo siguiente:
Let's imagine that a friend tells me the following:
Caption 44, Carlos explica - Diminutivos y Aumentativos Cap 2: Definiciones generales
Play Caption
It's also important to remember how pronouns are combined when using this verb. You must place reflexive or indirect object pronouns first, and then direct object pronouns right next to the verb. In the following example te replaces an indirect object (you) and lo (it) replaces a direct object:
Te lo digo de corazón.
I tell [it to] you from the heart.
Caption 25, Documental de Alejandro Fernandez - Viento A Favor
Play Caption
The past tense dijo (he/she/it said) is another useful form of this verb. For example, you can use it to talk about what someone told you in the past. The expression me lo dijo (he/she/it told it to me) is worth learning:
¡Es verdad, pana, mi hermano me lo dijo!
It's true, pal, my brother told it to me!
Caption 45, NPS No puede ser - 1 - El concurso - Part 3
Play Caption
No le digas (don’t tell him/her) and no me digas (don’t tell me) are also useful:
¡No le digas, Candelario!
Don't tell him, Candelario!
Caption 14, Guillermina y Candelario - La Isla de las Serpientes
Play Caption
Another fixed expression is se dice (it's said, one says), which is equivalent to dice la gente(people say):
Bueno y se dice que la mujer tiene un sexto sentido
Well, and one says that a woman has a sixth sense
Caption 16, Club de las ideas - Intuición - Part 1
Play Caption
The same phrase, se dice, can also be used to talk about the correct pronunciation of a word, or its meaning in a different language. For example:
Buenos días se dice "bonjour" en Francés | "Bonjour" is good morning in French.
No se dice "soy contento", se dice "estoy contento" | You don't say "soy contento," you say "estoy contento" (I'm happy).
You can find many more examples of the verb decir in our catalog. You just need to type the form of the verb that you want to practice in the search tool to start learning real Spanish from real speakers in real situations!

The Spanish verb llevar has many different meanings. It's also used in many idiomatic phrases. Let's study some examples since this is a very popular and useful verb.
The basic meanings of llevar is "to carry " or "to take":
Tengo que llevar a mi hijo al doctor - I have to take my kid to the doctor.
Ella lleva una carga muy pesada - She carries a very heavy burden.
Sometimes the verb llevar translates as "to bring":
No [te] olvides [de] llevar un regalo a la fiesta de Lucía / Don't forget to bring a gift to Lucia's party.
This can be a little confusing for English speakers, since traer and llevar actually mean opposite things in Spanish. The verb traer involves carrying something to the speaker's location, while llevar means to carry something from the speaker's location to a different place. So, to use the same example, if you are already at Lucía's party or, let's say, she is your roomie, you must say: No [te] olvides [de] traer un regalo a la fiesta de Lucía (Don't forget to bring a gift to Lucia's party).
But the verb llevar has many other interesting uses. For example, it's used to express the idea of having been doing something for a period of time. In this case, it's very common to combine llevar with the preposition ya (already):
Yo ya llevo veintitrés años aquí ya.
I have already been here for twenty-three years now.
Caption 65, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa - Part 18
Play Caption
Llevar can also be used to express duration. This is easy to learn since English also uses "to take" for the same purpose:
tenemos que teñirlo, esto pues, nos lleva un ratito,
we have to dye it, this well, it takes us a little while,
Caption 68, Animales en familia - Un día en Bioparc: Microchip para Nacahué - Part 1
Play Caption
As you can see, this use of llevar frequently involves using reflexive pronouns. But you don't always need them. Compare, for example:
Hacer la tarea lleva mucho tiempo / Doing homework takes a lot of time.
Hacer la tarea me lleva mucho tiempo / Doing homework takes me a lot of time.
Llevar also means"to wear":
¿Por qué lleváis guantes?
Why do you wear gloves?
Caption 46, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa - Part 5
Play Caption
By the way, the verb traer (to bring) is sometimes used the same way:
por eso... traen pantalones
that's why... they wear pants
Captions 47-48, El Ausente - Acto 2 - Part 3
Play Caption
And the verb llevar also means "to lead." For example: ¿Llevas una vida saludable? (Do you lead a healthy life?).
Finally, there's an expression used in Mexico that derives from this last meaning: ahí la llevas. It literally means something like "there, you are leading it" but it means that the person speaking is telling you that you are doing your work well. It's very common to use this expression as an ironic remark that means exactly the opposite, so be careful:
No te rindas, hijo. Ahí la llevas. / Don't give up, son. You are doing well.
¿Otra vez borracho? Bueno, tú síguele. Ahí la llevas. / Drunk again? Well, keep going. You are on the right track... not.

Let's continue our series on the use of the verbs ser and estar, now focusing on some examples using the subjunctive to express wishes, or to refer to hypothetical situations. The present subjunctive for the first person singular yo (I) is esté for the verb estar and sea for the verb ser. Here're some examples of first person singular sea and esté:
Mamá quiere que [yo] sea doctor / Mom wants me to be a doctor.
Mi hermana piensa que es mejor que [yo] sea dentista / My sister thinks it's best for me to be a dentist.
Lola me pide que [yo] esté tranquilo / Lola asks me to be calm.
Imagino que es mejor que no [yo] esté preocupado / I imagine it's better for me not to beworried.
Note that it's very common to use the pronoun que (that) before the subjunctive. In fact, some Spanish speakers learn to conjugate the subjunctive altogether with this pronoun, like: que yo sea, que tú seas, etc. or que yo esté, que tú estés, etc. to differentiate it from the indicative.
The forms sea and esté are also used for the third person singular, which is very convenient since you can use it to talk about wishes or hypothetical situations pertaining to other people, things, and ideas. For example:
Entonces, para que sea una sorpresa también.
So, for it to be a surprise also.
Caption 12, 75 minutos - Gangas para ricos - Part 10
Play Caption
Quiero comprar un barco que sea capaz de... de hacer travesías largas.
I want to buy a boat that is capable of... of making long voyages.
Captions 72-73, 75 minutos - Gangas para ricos - Part 20
Play Caption
Y que ya no sea Belanova el grupo de bajo, computadora y voz.
So that Belanova won't be the group of the bass, computer and voice any longer.
Caption 13, Belanova - Entrevista - Part 4
Play Caption
And with esté:
Ya la llamaremos cuando la doctora esté disponible.
We'll call you when the doctor is available.
Caption 42, Cita médica - La cita médica de Cleer - Part 1
Play Caption
Son tres modos que se usan para pedirle a alguien que esté alerta.
There are three ways that are used to ask someone to be alert.
Caption 27, Carlos comenta - Confidencial - Vocabulario y expresiones
Play Caption
Para que la aceituna esté en condiciones para envasar el lunes.
So that the olives are in condition for packing on Monday.
Caption 35, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa - Part 19
Play Caption
Finally, there's a very common and useful expression that uses sea: o sea, which is used to clarify or explain something. This expression translates as "in other words," "meaning," and other similar phrases.
O sea, que te vas a quedar sin marido durante tres meses.
In other words, you are going to be without a husband for three months.
Caption 27, 75 minutos - Del campo a la mesa - Part 3
Play Caption